Yamaha Robot
About the plugin
The Yamaha Robot plugin allows you to connect a Yamaha RCX 3 series robot controller during simulation and exchange data. For example, a program running in a virtual or physical Yamaha controller can drive the joints of a Yamaha robot in a simulation, read data from sensors, and set outputs for picking and placing products.
The plugin is associated with the Connectivity feature of Visual Components Premium and can connect to one or more Yamaha robot controllers. The simplified workflow is the following:
- Add server
- Connect to the server
- Map variables
- Run the simulation
Terminology
- RCX-Studio – Support software for the RCX series of robot controllers made by Yamaha.
- RCX3-SDK – Software development kit used for communicating with a RCX 3 controller.
- I/O (Input/Output).
Read and Write Support
Read and Write table
| Type | Read | Write | Notes |
| Robot controller input variables DI and SI |
Yes |
No |
|
| Robot controller output variables DO, LO, MO, SO and TO |
Yes |
Yes |
|
| Current joint values from any robot of the connected controller |
Yes | No | Per safety reasons |
Requirements
The Yamaha Robot plugin supports local and remote connections to a Yamaha controller. This requires Visual Components Premium and the RCX3-SDK to be installed on the same PC.
Note: RCX-Studio is not required to connect to a real robot, only the RCX3-SDK.
Setup
- Check that your host PC meets the requirements.
- Access the Yamaha robot controller.
- The plugin connects to the robot controller, so the virtual or physical robot controller should be accessible via a direct network connection (IP address) and have a 5000x port assigned to it.
- Note that a simulated controller in RCX-Studio is considered to run in offline mode.
- When RCX-Studio is connected to a physical controller, you have the option to run it in online mode. A connection is possible in either offline or online mode.
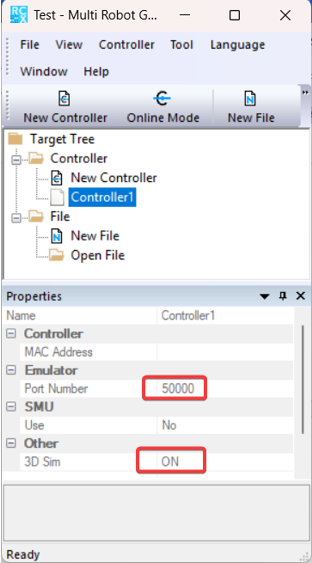
- For the controller, make sure Motor Power is turned on which is required for a connection. If connected and Motor Power is turned off, the connection is lost.
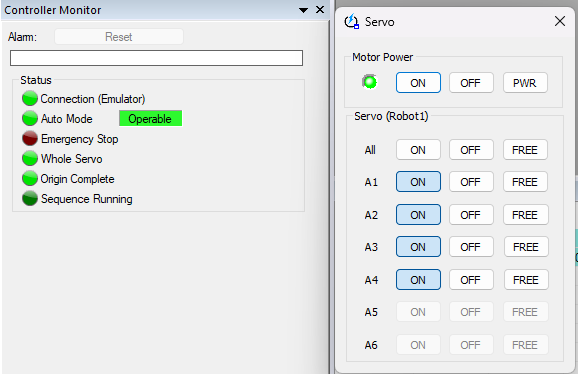
- In Visual Components add a new server with the plugin. Remember to use the port number assigned to the controller for the connection, for example 50000.
- Connect to the controller. Upon successful connection, you will receive feedback in the Output panel about the controller, its robots and I/O.
- If you plan to simulate a robot with rotational joints that uses degrees:
- Open matching robot driver parameters window from RCX-Studio.
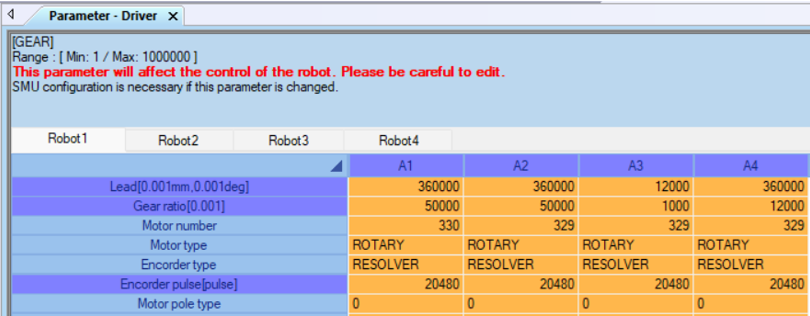 Driver Parameters window in RCX-Studio
Driver Parameters window in RCX-Studio - Open Visual Components Yamaha server Properties.
- Add robot and Axis parameters.
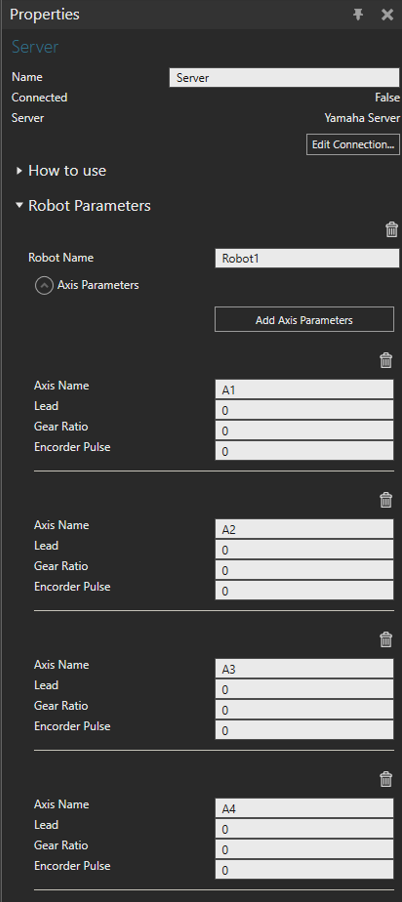 Axis Parameter panel in Visual Components
Axis Parameter panel in Visual Components
Yamaha Server Properties - Insert matching parameters from the RCX driver window to connectivity server axis parameters
- Open matching robot driver parameters window from RCX-Studio.
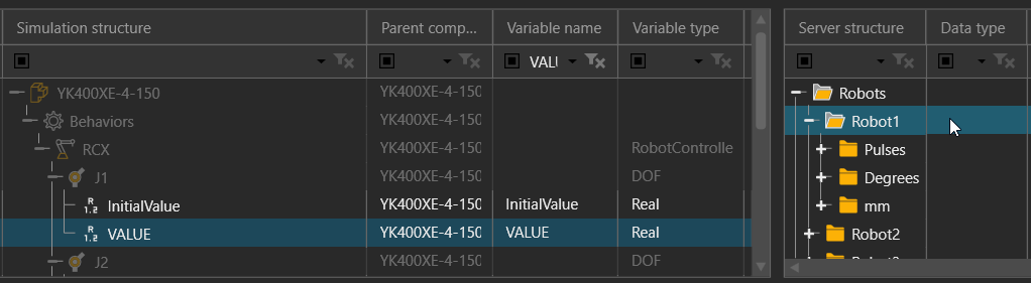
- Map the variables.
- For example, map the VALUE property of each degree of freedom (DOF)/Joint of the robot component to a joint of the corresponding mechanical unit in the controller. This way, the controller drives the robot in the 3D world.
- Pulses correspond to the pulse values from the controller.
- Degrees are converted from pulses since the RCX3-SDK does not provide a direct way to get degree values.
- The conversion formula is:
Degree = (Pulse)*(Lead/(Encoder Pulse*Gear))
And the Lead, Encoder, Pulse and Gear values are defined in the config file for the connector. - The mm are the translational values from the controller.
- For simulating actions such as grasp/release, map the outputs of the robot component for those actions to the I/O of the controller you will use for those actions.
- For example, map the VALUE property of each degree of freedom (DOF)/Joint of the robot component to a joint of the corresponding mechanical unit in the controller. This way, the controller drives the robot in the 3D world.
- Run the simulation.
- Simulate to start the exchange of data.
Note: In the Connected Variables panel, the Prepared value column can be used to set values for testing.
- Simulate to start the exchange of data.
Capabilities
You can verify the capabilities of the Yamaha Robot plugin and subsequent server connections in the Properties panel.
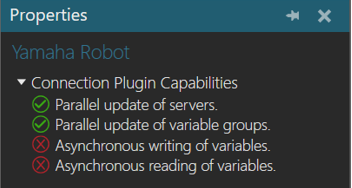
Plugin
- In the Connectivity Configuration panel, select Yamaha Robot.
- In the Properties panel, expand Connection Plugin Capabilities.
Server
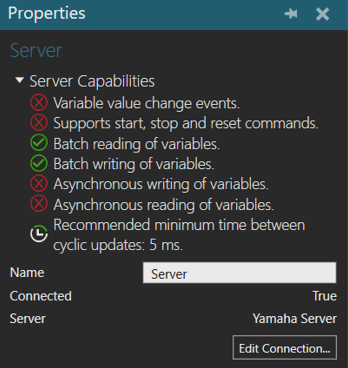
- In the Connectivity Configuration panel, expand Yamaha Robot, and then select an active server connection.
- In the Properties panel, expand Server Capabilities.
Connection Settings
A Yamaha Robot plugin connection requires a Yamaha robot controller to have an IP address and port number. Each connection in Visual Components is a client to the controller and not meant to remotely operate the robot.
Error handling
- If the connection to the controller is lost, the exchange of data will stop.
- The plugin expects an event to be received from the controller in such cases.
- If the event is not received, you might need to manually disconnect Visual Components from the controller and then attempt to reconnect to verify that the connection is lost.
- If the robot in Visual Components is not moving as expected, do the following.
- First, check that the robot joint values are mapped to the correct values on the controller.
- Next, check that the driver settings in the config file are correct and match the target robot of the controller.
- An RCX 3 series controller can manage multiple robots.
- By default, the config file of the connector has an entry for one robot, and those settings would correspond to the first indexed robot of the connected controller.
- Add entries for multiple robots as needed and then test again.
- Be aware of how signals are used in your Yamaha project when attempting to write those signals during simulation. When attempting to write a system variable, be aware of its range of values since a value outside of that range would generate an error or the variable itself might be locked.
Limitations
Joint values cannot be written to the robot controller per safety reasons.
Compatibility
The Yamaha Robot plugin was developed using RCX3-SDK and supports a connection to any Yamaha robot that is compatible with that technology.
Supported data types
The Yamaha Robot plugin supports access to digital signals and mechanical units joint data.
| Yamaha Robot Type | .NET Type |
| Digital Input and Serial Input | System.Boolean |
| Digital Output, Lock Output, Managed Output, Serial Output, Timer Output | System.Boolean |
| Joint | System.Double |
Post Processing the Robot Program
Postprocessor
If you need to translate robot programs from your Visual Components model to the native controller, you can use the Postprocessor.
Note: The Postprocessor is available in the following products:
- Visual Components Premium
- Visual Components Premium OLP
- Visual Components Professional OLP
- Visual Components Robotics OLP
For more information on postprocessing using a Visual Components OLP product, see Translate robot program.
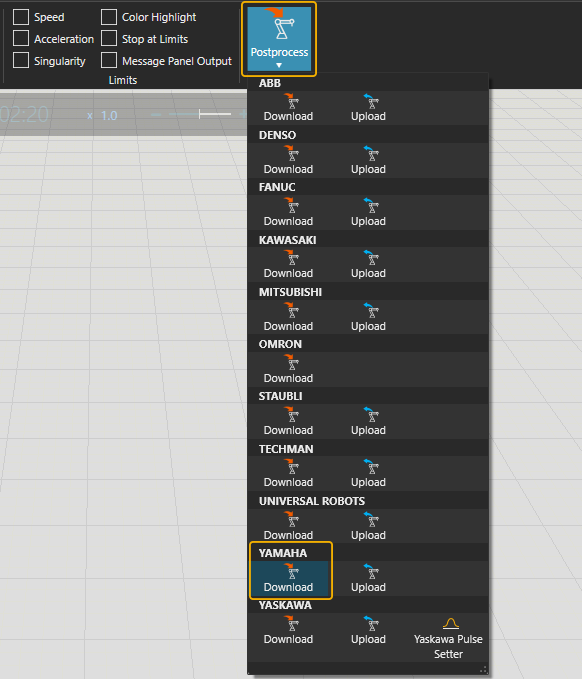
To translate the robot program for the real robot controller:
- Click the robot (or another device) which program you want to translate.
- Click Postprocess from PROGRAM ribbon tools.
- Click Download under the correct robot brand name.
- Browse the folder where you want to save the program file and give name for the file.
-
Click Save.
The file can be transferred to the robot controller
Note: In real robots, run only the robot programs that are translated from calibrated models. Otherwise, there can be unpredictable collisions and errors when executing the program.
For more information check the Visual Components Robotics OLP robot brand specific manuals on the Visual Components OLP Extranet.